Introduction to Intelligent Virtual Assistants
Intelligent Virtual Assistants (IVAs) are one of the most significant innovations in modern technology, reshaping how individuals and businesses interact with digital systems. Unlike traditional virtual assistants that can only perform pre-programmed tasks, intelligent virtual assistants leverage artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP) to understand context, learn from interactions, and provide personalized responses. This allows users to interact with their devices more naturally and efficiently, whether through voice, text, or a combination of both.
IVAs have evolved tremendously over the past decade. Early virtual assistants, like basic chatbots, could only respond to simple commands such as setting alarms or checking the weather. Today, intelligent virtual assistants like Google Assistant, Siri, and enterprise-focused IVAs such as IBM Watson Assistant can handle complex workflows, manage schedules, perform research, and even assist in decision-making processes. This evolution reflects the broader trend of AI becoming an integral part of everyday life, both at home and in the workplace.
For businesses, intelligent virtual assistants provide more than just automation—they enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and improve customer experiences by providing instant, accurate support. For individuals, they simplify daily routines, provide reminders, and even suggest proactive actions based on user behavior.http://aibygoogl.com
The rise of intelligent virtual assistants also sparks important discussions around ethics, privacy, and AI reliability. While IVAs are powerful, their reliance on data and learning algorithms means users must be aware of how their information is collected and used. Nevertheless, the potential of IVAs to transform productivity, communication, and workflow management remains unmatched.
In the sections ahead, we will dive deeper into how intelligent virtual assistants work, their popular types, key benefits, challenges, and emerging trends. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of IVAs and how they are shaping the future of human-computer interaction.
How Intelligent Virtual Assistants Work
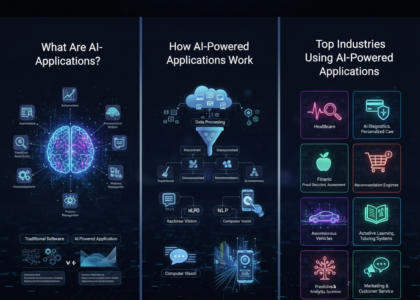
Intelligent Virtual Assistants (IVAs) operate at the intersection of multiple advanced technologies, enabling them to understand, learn, and respond intelligently to human commands. Unlike basic virtual assistants that follow pre-set scripts, IVAs analyze context, learn from interactions, and adapt over time, making them far more versatile and capable.
Core Technologies Behind IVAs
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI allows IVAs to perform tasks that traditionally required human intelligence. Machine learning enables them to learn from past interactions, improving accuracy and efficiency. For example, if a user frequently asks their IVA to schedule meetings on Mondays, the assistant can start suggesting Monday slots proactively. - Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP is a key technology that allows IVAs to understand human language in text or speech form. It breaks down sentences into meaningful components, identifies intent, and extracts actionable information. This technology is what allows IVAs to respond naturally rather than providing rigid, robotic replies. - Speech Recognition and Synthesis:
Many intelligent virtual assistants interact via voice commands. Speech recognition converts spoken words into text, while speech synthesis allows the IVA to respond verbally. These technologies work together to create a conversational experience that feels seamless and human-like. - Context Awareness and Decision-Making Algorithms:
Unlike traditional assistants, IVAs can maintain context across interactions. For example, if a user says, “Remind me about the meeting tomorrow,” and later asks, “What about the one next week?” the IVA can intelligently infer the second reference and provide the correct response. Advanced IVAs also use decision-making algorithms to offer recommendations or take actions autonomously based on patterns and data.
How IVAs Understand and Respond
IVAs follow a multi-step process to understand and respond to user queries:
- Intent Recognition: IVAs identify the purpose behind a user’s command, such as setting a reminder, answering a question, or controlling a smart device.
- Entity Extraction: They identify key details like dates, times, locations, or names from user input.
- Response Generation: Based on intent and entities, the IVA generates a response. This could be providing information, performing an action, or asking clarifying questions.
- Learning and Adaptation: IVAs track user behavior and feedback to improve future interactions. Over time, this allows them to provide more accurate, personalized assistance.
Example: If you ask an IVA, “Book a flight to New York next Friday,” it will:
- Recognize the intent: booking a flight
- Extract entities: location (New York) and date (next Friday)
- Provide options, confirm the booking, and store the information for future references
This ability to understand context, learn from interactions, and provide proactive assistance is what distinguishes intelligent virtual assistants from standard digital helpers.
Popular Intelligent Virtual Assistants in 2026
In 2026, intelligent virtual assistants have become increasingly sophisticated, offering a wide range of functionalities for both personal and professional use. From consumer-focused IVAs like Siri and Alexa to enterprise solutions such as IBM Watson Assistant, these AI-powered tools are transforming how we manage daily tasks, workflow automation, and customer interactions. Let’s explore the most popular IVAs and their applications.
Consumer-Focused Intelligent Virtual Assistants
Consumer IVAs are designed for personal use, integrating seamlessly into smartphones, smart speakers, and other devices. Some of the most widely used IVAs include:
- Siri (Apple): Siri continues to be a popular choice for Apple users, offering voice-activated commands, reminders, and device control. Its integration with the Apple ecosystem allows seamless management of apps, calendars, and smart home devices.
- Google Assistant: Known for its superior natural language understanding and search capabilities, Google Assistant excels in answering questions, setting reminders, and providing proactive suggestions based on user behavior.
- Amazon Alexa: Alexa dominates the smart home space, controlling lights, thermostats, and appliances. It also supports third-party skills, allowing users to extend its functionality to music, shopping, and entertainment.
- Cortana (Microsoft): While no longer a primary consumer IVA, Cortana remains integrated into Windows devices, offering productivity features like calendar management and email assistance.
Key Features of Consumer IVAs:
- Voice commands and conversational interaction
- Integration with smartphones, wearables, and smart home devices
- Personalized suggestions based on user habits
- Multilingual support and context-aware responses
Enterprise and Business Intelligent Virtual Assistants
Businesses leverage IVAs to automate repetitive tasks, improve customer service, and enhance employee productivity. Popular enterprise IVAs include:
- IBM Watson Assistant: Designed for enterprise applications, Watson can understand complex queries, integrate with multiple platforms, and provide analytics-driven responses. It’s widely used in customer service, healthcare, and banking.
- Amelia (IPsoft): Amelia is an AI assistant for enterprises that can handle sophisticated customer interactions, resolve issues, and escalate problems intelligently.
- x.ai: Focused on scheduling and workflow automation, x.ai handles meeting planning, calendar management, and email coordination with minimal human intervention.
Business IVA Advantages:
- Automates customer support, reducing response times
- Provides actionable insights through data analysis
- Supports multilingual communication for global teams
- Integrates with CRM, ERP, and other business tools
Niche or Specialized Intelligent Virtual Assistants
Certain IVAs are designed for industry-specific tasks:
- Healthcare: IVAs like Buoy Health assist in symptom checking, patient triage, and medical information dissemination.
- Finance: AI assistants such as Cleo help users manage personal finance, monitor spending, and provide investment advice.
- Productivity & Workflow: Tools like Clara and Notion AI automate scheduling, note-taking, and task management.
These specialized IVAs not only streamline tasks but also enhance decision-making by providing accurate, context-aware recommendations tailored to industry requirements.
Table: Comparison of Popular Intelligent Virtual Assistants
| IVA | Primary Use | Key Feature | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Siri | Personal | Apple ecosystem integration | Consumers |
| Google Assistant | Personal/Smart Home | NLP & proactive suggestions | Consumers |
| Alexa | Smart Home | Voice control + third-party skills | Consumers |
| Watson Assistant | Enterprise | Data-driven insights | Businesses |
| Amelia | Enterprise | Intelligent customer support | Businesses |
| x.ai | Productivity | Meeting & workflow automation | Businesses |
| Buoy Health | Healthcare | Symptom checking & guidance | Medical |
| Cleo | Finance | Personal finance management | Individuals |
By understanding the different types of IVAs available today, users and businesses can choose solutions that maximize productivity, efficiency, and overall user satisfaction.
Key Benefits of Using Intelligent Virtual Assistants
Intelligent Virtual Assistants (IVAs) offer a wide range of benefits for both individuals and businesses. By leveraging AI, machine learning, and natural language processing, these assistants not only save time but also improve decision-making, productivity, and overall efficiency. Understanding these benefits can help users make informed choices about adopting IVAs in daily life or business operations.
Benefits for Individuals
- Time-Saving and Productivity Improvements:
IVAs handle repetitive tasks such as setting reminders, sending messages, scheduling appointments, or checking the weather. By automating these tasks, users can focus on higher-priority activities, ultimately improving productivity. For instance, a study by Gartner shows that using virtual assistants can reduce scheduling and administrative tasks by up to 30%. - Personalized Assistance:
Intelligent virtual assistants learn from user behavior and preferences. Over time, they can offer proactive suggestions, such as recommending a meeting time based on your calendar patterns or suggesting playlists and reminders tailored to your routine. - Access to Information Anywhere, Anytime:
With voice commands and mobile integration, IVAs provide instant access to information without the need to manually search. Users can ask complex questions, retrieve directions, check the latest news, or control smart home devices—all through a natural conversational interface.
Benefits for Businesses
- Automating Customer Service and Support:
IVAs can handle repetitive customer inquiries, providing instant responses through chatbots or voice assistants. This reduces waiting times and frees up human agents to handle more complex issues. For example, companies like Sephora and HDFC Bank use AI-powered assistants to manage FAQs, order tracking, and troubleshooting. - Cost Efficiency:
By automating routine tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs and improve operational efficiency. IVAs can manage tasks such as appointment scheduling, data entry, and client follow-ups without human intervention, offering significant savings over time. - Data-Driven Decision Making:
Enterprise IVAs can analyze large volumes of data to provide insights, detect trends, and predict outcomes. This allows businesses to make smarter decisions, optimize processes, and identify growth opportunities. For instance, IBM Watson Assistant integrates with CRM systems to provide actionable analytics based on customer interactions. - Enhanced Productivity Across Teams:
IVAs can assist employees in managing emails, setting reminders, booking meetings, and providing summaries of key data. Tools like x.ai or Clara Labs help teams stay organized and reduce administrative workload, which enhances overall workplace productivity.
Additional Advantages
- Consistency and Accuracy: IVAs perform tasks without human errors, ensuring reliable outputs.
- 24/7 Availability: Unlike humans, IVAs can work around the clock, providing support at any time.
- Scalability: Businesses can scale virtual assistant services easily to handle increased demand without proportional increases in costs.
Case Study:
Sephora’s chatbot IVA increased customer engagement by 11% while reducing response times by over 50%.
IBM Watson Assistant helped a major bank automate 70% of repetitive queries, saving thousands of man-hours annually.
Challenges and Limitations of Intelligent Virtual Assistants
While intelligent virtual assistants (IVAs) provide remarkable benefits, they are not without challenges. Understanding the limitations is critical for both individuals and businesses before adopting them fully. These challenges range from technical issues to ethical and privacy concerns.
1. Privacy and Data Security Concerns
IVAs rely heavily on personal and organizational data to function effectively. They collect, store, and analyze user interactions to improve performance and provide personalized assistance. However, this raises significant privacy risks:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive data
- Data breaches or leaks
- Use of personal data for targeted advertising
For example, incidents where smart assistants accidentally recorded conversations have highlighted the need for robust data encryption and privacy policies. Users and businesses must ensure that the IVA platform follows strict security standards and complies with regulations like GDPR or HIPAA for healthcare-related IVAs.
2. Misinterpretation of Commands or Context
Even the most advanced IVAs can struggle to fully understand nuanced commands, regional accents, slang, or ambiguous instructions. Misinterpretation can lead to:
- Incorrect task execution
- Frustration for users
- Reduced trust in the system
While IVAs improve over time through machine learning, they are still not perfect and require careful monitoring and occasional human oversight.
3. Dependence on Internet Connectivity and Cloud Services
Most intelligent virtual assistants rely on cloud computing for processing commands and accessing large datasets. Without stable internet connectivity, IVAs may fail to respond or provide outdated information. This can be a critical limitation for users in areas with unreliable connectivity or businesses that need uninterrupted operations.
4. Ethical and Bias Considerations
AI systems, including IVAs, can unintentionally inherit biases from training data, leading to:
- Biased recommendations
- Unfair decision-making in sensitive applications
- Misrepresentation of information
Ethical concerns also include transparency, accountability, and ensuring that AI does not replace human judgment in critical situations. Companies must regularly audit AI systems to mitigate bias and maintain ethical standards.
5. Integration and Compatibility Issues
Some IVAs may struggle to integrate with existing software, devices, or enterprise systems. This can limit their utility, requiring additional development resources or adjustments to workflows. For businesses, integration challenges can slow down adoption and reduce ROI.
6. Learning Curve and User Adaptation
Although IVAs are designed to simplify tasks, there is a learning curve. Users must understand how to interact with the system effectively. Employees in businesses may require training to use enterprise IVAs efficiently, which can involve time and cost.
Example:
A study by Deloitte found that while 72% of businesses planned to adopt AI assistants, 45% faced integration challenges and 38% cited employee training as a significant barrier.