Introduction
Cognitive AI systems represent the next evolution of artificial intelligence, combining machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), and cognitive computing to simulate human thought, reasoning, and decision-making. Unlike traditional AI systems, which rely on rigid rules or predefined algorithms, cognitive AI systems are capable of learning from data, understanding context, and adapting to new situations. This makes them invaluable across multiple domains, including business, healthcare, education, and daily life.
These systems are designed to augment human intelligence rather than replace it. They analyze vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, recognize patterns, predict outcomes, and even offer recommendations. For example, in healthcare, a cognitive AI system can review thousands of medical records, identify anomalies, and suggest treatment plans, assisting doctors in making more accurate and timely decisions.http://aibygoogl.com
Key benefits of cognitive AI systems include:
- Enhanced decision-making: They provide insights based on large datasets, which humans might overlook.
- Automation and productivity: Cognitive AI automates routine and complex tasks, freeing humans for creative and strategic work.
- Innovation and personalization: They enable personalized experiences, smarter products, and innovative solutions in multiple industries.
- Scalability: Cognitive AI systems can handle increasing workloads without proportional human input, making them ideal for growing organizations.
Fact: According to a report by PwC, businesses that integrate cognitive AI systems into their operations can see productivity gains of up to 40%, with significant improvements in decision-making speed and accuracy.
In this article, we will explore what cognitive AI systems are, how they work, their applications, benefits, challenges, and future trends. By the end, you will have a complete understanding of this transformative technology and how it can be applied in real-world scenarios.
What Are Cognitive AI Systems?
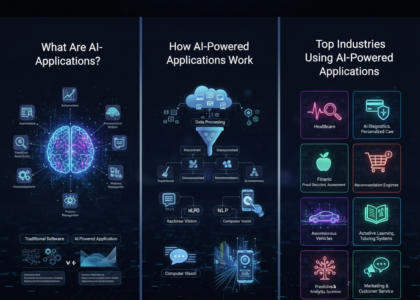
Cognitive AI systems are advanced artificial intelligence platforms designed to mimic human thought processes. Unlike traditional AI, which operates based on pre-defined rules, cognitive AI systems can reason, learn from data, understand context, and make decisions independently. They combine multiple AI technologies, including machine learning, natural language processing (NLP), neural networks, and knowledge representation, to simulate aspects of human cognition.
At their core, cognitive AI systems are problem-solving tools. They are capable of interpreting complex data, recognizing patterns, and generating insights that would be impossible—or extremely time-consuming—for humans to produce manually. This makes them highly valuable in sectors that require high-level decision-making, predictive analytics, and adaptive learning.
Key Features of Cognitive AI Systems
- Learning and Adaptation
- Cognitive AI systems continuously learn from historical and real-time data, improving their accuracy over time.
- Example: AI in customer service learns from past conversations to improve response quality.
- Reasoning and Decision-Making
- These systems analyze multiple factors, weigh alternatives, and suggest or take actions based on their analysis.
- Example: Cognitive AI in finance evaluates risk factors before approving a loan.
- Natural Language Understanding (NLP)
- Enables AI to interpret, process, and respond to human language, both written and spoken.
- Example: Virtual assistants like IBM Watson can answer complex queries in natural language.
- Contextual Understanding
- Cognitive AI systems understand context, enabling more accurate responses and predictions.
- Example: In healthcare, AI considers patient history, lab results, and current symptoms for better diagnostics.
- Self-Improvement
- Cognitive AI can refine its algorithms autonomously, becoming smarter as it interacts with more data.
Types of Cognitive AI Systems
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cognitive Computing Platforms | Integrate AI with human-like reasoning and decision-making | IBM Watson for healthcare |
| AI-Powered Virtual Assistants | Understand queries, perform tasks, and learn user preferences | Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant |
| Cognitive Analytics Systems | Analyze large datasets and generate actionable insights | Cognitive AI for business intelligence |
| Hybrid Cognitive AI Systems | Combine multiple AI methods such as NLP, machine learning, and reasoning | AI-powered financial risk assessment tools |
How Cognitive AI Systems Simulate Human Intelligence
Cognitive AI systems are designed to replicate human cognitive functions such as learning, reasoning, and decision-making:
- Learning from Data: Uses machine learning to identify patterns and relationships.
- Understanding Context and Intent: NLP and semantic analysis allow the system to interpret nuances in text or speech.
- Problem-Solving: Combines multiple data sources and reasoning models to recommend solutions.
- Adaptive Responses: Adjusts strategies and predictions based on new inputs and changing environments.
Quote: “Cognitive AI systems are not here to replace human intelligence—they are here to augment it, providing insights and decision-making support at a scale and speed humans cannot achieve alone.” – Gartner, 2025
How Cognitive AI Systems Work
Cognitive AI systems function by combining advanced AI technologies with human-like reasoning to analyze, learn, and make decisions. Unlike traditional AI, which follows pre-set rules, cognitive AI systems can interpret unstructured data, adapt to new inputs, and improve over time. Understanding how these systems work helps organizations and individuals leverage them effectively.
Core Technologies Behind Cognitive AI Systems
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Machine learning enables AI to learn from historical and real-time data without explicit programming.
- Example: In banking, ML-powered cognitive AI detects patterns in transaction data to prevent fraud.
- Deep Learning and Neural Networks
- Mimic human brain functionality to recognize patterns, images, and speech.
- Example: Cognitive AI in healthcare analyzes MRI scans to detect abnormalities faster than human radiologists.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- Allows AI to understand and respond to human language, including context and sentiment.
- Example: IBM Watson uses NLP to interpret complex medical queries and provide recommendations.
- Knowledge Representation and Reasoning
- Cognitive AI stores structured knowledge and applies logical reasoning to solve problems.
- Example: AI systems in legal tech analyze case law to suggest legal strategies.
- Predictive Analytics
- Cognitive AI uses historical and real-time data to forecast trends and outcomes.
- Example: Retailers use cognitive AI to predict customer demand and optimize inventory.
Role of Data in Cognitive AI Systems
Data is the foundation of any cognitive AI system. Without quality data, AI cannot learn or make accurate predictions. Key points about data:
- Volume: Cognitive AI systems require large datasets to detect patterns and insights.
- Quality: Clean, unbiased, and accurate data is essential for reliability.
- Variety: Combining structured and unstructured data (text, audio, images, numeric) improves system intelligence.
- Real-Time vs. Historical Data:
- Real-time data allows instant decision-making (e.g., autonomous vehicles).
- Historical data enables predictive analytics (e.g., trend forecasting in business).
Fact: According to Deloitte, organizations using AI-powered cognitive analytics are 5 times more likely to make faster, accurate decisions than those relying solely on human analysis.
Cognitive AI Decision-Making Process
Cognitive AI systems make decisions through a structured multi-step process:
- Data Collection: Gather structured and unstructured data from multiple sources.
- Data Analysis: Identify patterns, relationships, and anomalies.
- Contextual Understanding: Consider the situation, historical patterns, and intent.
- Reasoning: Apply predictive and prescriptive analytics to generate recommendations.
- Decision or Action: Execute the decision autonomously or provide insights for human review.
- Continuous Learning: Refine algorithms and improve accuracy based on feedback and new data.
Real-Time vs. Offline Cognitive AI Systems
| Type | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Systems | Process incoming data instantly to make immediate decisions | Self-driving cars adjusting to traffic |
| Offline Systems | Analyze stored data to provide long-term insights or predictions | AI predicting customer buying trends |
Both approaches are critical. Real-time cognitive AI is essential for urgent tasks, while offline systems are ideal for strategic planning and predictive modeling.
Applications of Cognitive AI Systems
Cognitive AI systems are transforming industries and daily life by providing intelligent decision-making, automation, and predictive capabilities. Their ability to analyze complex data, understand context, and provide actionable insights makes them invaluable across business, healthcare, education, and personal use.
Business and Enterprise Applications
Cognitive AI systems are widely used in businesses to improve efficiency, decision-making, and customer experience:
- AI-Powered Customer Support
- Virtual assistants and chatbots handle routine queries and provide personalized responses.
- Example: H&M uses cognitive AI chatbots to guide online shoppers and answer product questions in real-time.
- Predictive Analytics for Business Decisions
- Analyze historical and real-time data to forecast sales, demand, and market trends.
- Example: Retailers like Walmart use AI to optimize inventory and reduce stockouts.
- Risk Assessment and Fraud Detection
- Cognitive AI identifies suspicious patterns and predicts potential risks.
- Example: Mastercard uses AI to prevent fraudulent transactions instantly.
- Process Automation
- Automates repetitive workflows such as invoice processing, HR tasks, and supply chain management.
- Cognitive AI systems continuously optimize these processes to improve efficiency.
Healthcare Applications
Cognitive AI systems are revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnostics, treatment planning, and patient care:
- Diagnostics and Imaging Analysis
- AI systems can analyze medical images, detect anomalies, and suggest diagnoses.
- Example: Zebra Medical Vision uses AI to identify early signs of diseases like cancer and heart conditions.
- Predictive Patient Care
- Predicts patient readmissions and identifies at-risk patients before complications occur.
- Example: Hospitals use AI to schedule interventions for high-risk patients, improving outcomes.
- Drug Discovery and Personalized Medicine
- Cognitive AI analyzes chemical data and patient history to speed up drug development and recommend personalized treatments.
- Example: IBM Watson Health accelerates drug research and tailors treatment plans.
Education Applications
Cognitive AI is also making education smarter and more personalized:
- Intelligent Tutoring Systems
- Offers adaptive learning paths based on student performance.
- Example: Carnegie Learning uses AI to help students master mathematics efficiently.
- Adaptive Learning Platforms
- Adjusts lessons in real-time based on student engagement and progress.
- Administrative Automation
- Automates grading, attendance tracking, and resource allocation to save educators time.
Everyday Life Applications
Cognitive AI systems are increasingly integrated into daily life:
- Virtual Personal Assistants
- Assist with scheduling, reminders, and information retrieval.
- Example: Google Assistant and Amazon Alexa learn user habits and provide personalized suggestions.
- Smart Home Devices
- Cognitive AI adjusts temperature, lighting, and energy usage based on patterns.
- E-Commerce and Entertainment Recommendations
- AI analyzes behavior to suggest products, movies, or music, creating personalized experiences.
- Autonomous Vehicles
- Cognitive AI interprets traffic data and environment conditions to make safe driving decisions.
- Example: Tesla Autopilot uses cognitive AI for navigation, hazard detection, and adaptive responses.
Case Studies of Cognitive AI Applications
| Industry | Company/Example | Application | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | IBM Watson Health | AI-assisted diagnostics and treatment recommendations | Faster, more accurate diagnoses, personalized care |
| Retail | Walmart | Predictive inventory management and demand forecasting | Reduced stockouts, improved operational efficiency |
| Finance | Mastercard | Fraud detection and risk analysis | Immediate fraud prevention, enhanced security |
| Education | Carnegie Learning | Adaptive learning and intelligent tutoring | Improved student performance and engagement |
Benefits of Cognitive AI Systems
Cognitive AI systems are not just advanced technology—they are powerful tools that enhance decision-making, improve efficiency, and drive innovation. Their ability to analyze complex data, understand context, and learn over time provides significant advantages across industries and everyday applications.
1. Enhanced Decision-Making
Cognitive AI systems help organizations make data-driven and context-aware decisions:
- They analyze large datasets faster and more accurately than humans.
- Provide predictive insights, identifying trends, risks, and opportunities.
- Allow scenario testing and simulation for smarter planning.
Example: Financial institutions use cognitive AI to assess credit risk and detect anomalies in transactions, improving both speed and accuracy in decision-making.
Fact: A study by Accenture found that cognitive AI can improve decision-making by up to 40%, reducing errors and operational risks.
2. Improved Efficiency and Productivity
Cognitive AI systems automate repetitive and complex tasks, freeing human resources for creative and strategic work:
- Workflow automation in business and healthcare
- Faster data analysis and reporting
- Real-time monitoring and adjustments in operations
Example: Amazon’s warehouses use AI-driven robots and cognitive AI software to sort, package, and manage inventory, reducing processing time and operational errors.
3. Innovation and Competitive Advantage
By leveraging cognitive AI systems, organizations can innovate faster and gain a competitive edge:
- Identify new market trends and opportunities
- Develop personalized products and services
- Enhance customer experience with AI-driven personalization
Case Study: Starbucks uses cognitive AI to recommend beverages and promotions to customers based on purchase history, location, and preferences, increasing customer engagement and sales.
4. Cost Savings and Scalability
Cognitive AI systems allow businesses to scale operations efficiently while reducing costs:
- Lower operational costs through automation
- Predictive maintenance reduces downtime and repair expenses
- Handle growing workloads without proportional increases in staff
Example: General Electric uses cognitive AI for predictive maintenance in industrial machinery, saving millions annually in repair costs and reducing equipment downtime.
5. Improved Accuracy and Reliability
Cognitive AI reduces human error and ensures consistent and reliable outputs:
- Processes millions of data points without fatigue
- Recognizes patterns that humans might miss
- Provides evidence-based recommendations
Example: In healthcare, cognitive AI systems like Zebra Medical Vision analyze medical imaging with higher accuracy than traditional methods, helping doctors detect conditions earlier.
Challenges of Cognitive AI Systems
While cognitive AI systems offer tremendous benefits, implementing and managing them comes with several challenges. Understanding these challenges is essential for businesses, healthcare providers, educators, and other organizations seeking to adopt AI responsibly.
1. Ethical and Social Challenges
- Bias in AI Decisions
- Cognitive AI systems learn from historical and real-world data. If the data contains biases, the AI may produce unintended discriminatory outcomes.
- Example: AI recruitment tools have, in some cases, favored certain demographics due to biased training data.
- Privacy and Security Concerns
- Cognitive AI relies on large volumes of personal and organizational data, making security crucial.
- Improper handling can lead to data breaches or misuse of sensitive information.
- Job Displacement
- Automation of repetitive and analytical tasks may reduce demand for human labor in certain roles.
- However, cognitive AI also creates new jobs in AI development, data analysis, and strategy.
Quote: “The adoption of cognitive AI systems must include strong ethical guidelines to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability.” – World Economic Forum, 2025
2. Technical Challenges
- Complexity of AI Architectures
- Advanced cognitive AI systems involve machine learning, deep learning, NLP, and knowledge reasoning, which require expert implementation and management.
- Data Quality and Availability
- High-quality, clean, and relevant data is critical for accurate predictions. Poor data leads to errors and unreliable outputs.
- Integration with Existing Systems
- Deploying cognitive AI often requires modifying legacy systems or ensuring seamless interoperability across platforms.
3. Cost and Resource Constraints
- High Development and Implementation Costs
- Cognitive AI requires skilled teams, cloud infrastructure, and specialized software, which can be expensive for small and medium businesses.
- Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
- AI systems need ongoing updates, retraining, and supervision to maintain accuracy and performance.
- Infrastructure Requirements
- Cognitive AI often requires high-performance computing resources and robust data storage solutions.
4. Managing Expectations
- Many organizations overestimate what cognitive AI can deliver immediately.
- Cognitive AI systems require time to learn and optimize before delivering full value.
- Clear goal-setting and phased implementation are essential to avoid disappointment.
Fact: According to Gartner, nearly 85% of AI projects fail to deliver expected results due to inadequate planning, poor data quality, and lack of monitoring.
Implementing Cognitive AI Systems in Your Organization
Deploying cognitive AI systems effectively requires careful planning, data preparation, and a structured approach. When implemented correctly, these systems enhance efficiency, improve decision-making, and drive innovation.
Steps to Deploy Cognitive AI Systems
- Identify Organizational Needs
- Determine which processes or challenges could benefit most from cognitive AI.
- Example: A hospital may focus on diagnostic support, while a retail company might prioritize customer behavior analysis.
- Choose the Right AI Platforms and Tools
- Select cognitive AI software or platforms that align with your business objectives and technical capabilities.
- Examples: IBM Watson for healthcare, Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services for enterprise AI, or Google AI tools for analytics.
- Collect and Prepare Data
- Cognitive AI relies heavily on high-quality data.
- Ensure data is clean, structured, and includes both historical and real-time inputs.
- Example: In finance, transactional data must be accurate, complete, and formatted correctly.
- Train and Deploy the System
- Feed the AI system with datasets to teach it patterns and decision-making rules.
- Begin with pilot programs to validate accuracy before full deployment.
- Monitor, Evaluate, and Optimize Continuously
- Cognitive AI systems learn over time. Regularly monitor outputs, update models, and refine algorithms for better performance.
- Example: E-commerce companies continuously update recommendation engines based on new customer behavior data.
Best Practices for Implementing Cognitive AI
- Start Small with Pilot Projects
- Test cognitive AI on a limited scope to evaluate performance before scaling.
- Set Clear, Measurable Goals
- Define KPIs like improved decision accuracy, reduced processing time, or increased sales.
- Maintain Human Oversight
- Cognitive AI should augment, not replace, human judgment. Human supervision ensures ethical and accurate outcomes.
- Ensure Data Privacy and Security
- Protect sensitive data using encryption, anonymization, and strict access controls.
- Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
- Involve IT, operations, and business teams to ensure AI integrates seamlessly into workflows.
- Leverage External Expertise if Needed
- Partner with AI consultants, vendors, or universities to accelerate adoption and reduce risk.
Real-World Implementation Examples
| Industry | Company | Cognitive AI Application | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | IBM Watson Health | AI-assisted diagnostics and treatment planning | Faster, more accurate patient care |
| Retail | Amazon | Cognitive AI-powered inventory management | Reduced stockouts, optimized logistics |
| Finance | Mastercard | Fraud detection and risk assessment | Immediate fraud alerts, improved security |
| Education | Carnegie Learning | Adaptive learning platforms | Personalized learning, improved student outcomes |
Future of Cognitive AI Systems
The future of cognitive AI systems is both exciting and transformative. As AI technologies continue to advance, these systems will become smarter, more adaptive, and deeply integrated into industries, businesses, and daily life. Understanding emerging trends and potential impacts helps organizations and individuals prepare for the next wave of AI innovation.
Emerging Trends in Cognitive AI
- Explainable AI (XAI)
- Cognitive AI systems are becoming more transparent, allowing users to understand how decisions are made.
- Example: In healthcare, doctors can review AI-generated treatment recommendations along with the reasoning behind them, improving trust and adoption.
- Integration with Edge Computing
- AI is moving closer to data sources, enabling real-time processing on devices rather than centralized servers.
- Example: Smart cars using cognitive AI can process data on the vehicle for faster, safer responses.
- Hybrid Cognitive AI Models
- Combining machine learning, symbolic AI, and reasoning systems to handle more complex and nuanced problems.
- Example: Financial institutions using hybrid AI for fraud detection and market prediction.
- AI-Powered Autonomous Systems
- Cognitive AI will increasingly control autonomous vehicles, drones, and robotics with human-like reasoning and adaptability.
- Example: Delivery drones using cognitive AI can navigate dynamic environments and adjust routes in real-time.
- AI for Personalization at Scale
- AI will deliver highly personalized experiences in education, healthcare, entertainment, and e-commerce.
- Example: Streaming platforms like Netflix or Spotify may leverage cognitive AI to predict and adapt to evolving user preferences in real-time.
Potential Impact Across Industries
| Industry | Future Cognitive AI Application | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Real-time diagnostics, predictive patient care, precision medicine | Improved patient outcomes, reduced healthcare costs |
| Finance | AI-driven investment strategies, fraud prevention, risk management | Smarter decision-making, enhanced security |
| Education | Fully adaptive learning platforms, AI tutors with emotional recognition | Personalized learning, improved student performance |
| Retail & E-Commerce | Dynamic pricing, predictive inventory, personalized recommendations | Increased sales, optimized inventory management |
| Transportation | Autonomous vehicles, smart traffic management | Safer roads, reduced congestion and travel times |
Predictions for Businesses and Society
- Cognitive AI systems will increasingly augment human intelligence, rather than replace it.
- AI-powered analytics will enable smarter, data-driven strategies across all sectors.
- Cities, homes, and infrastructure will become smarter, using AI to optimize energy, traffic, and services.
- Ethical AI adoption will be critical, as widespread use raises privacy, bias, and governance concerns.
Fact: According to PwC, cognitive AI and automation could contribute over $15 trillion to the global economy by 2030, highlighting the massive transformative potential of these systems.