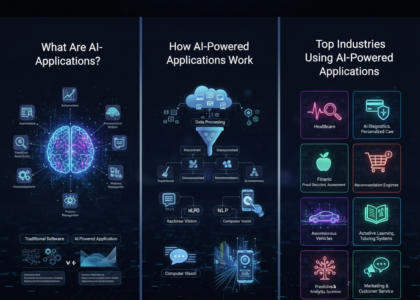
Introduction to Smart Automation Software
Smart automation software has emerged as one of the most transformative technologies for businesses and individuals alike. Unlike traditional automation systems, which perform repetitive tasks based on fixed rules, smart automation software leverages artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and intelligent workflow management to adapt, learn, and optimize processes over time. This makes it a critical tool for organizations aiming to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and scale operations without proportional increases in cost or workforce.
At its core, smart automation software is designed to automate complex processes by understanding workflows, predicting outcomes, and making decisions autonomously. For example, a sales team can use smart automation to automatically track leads, assign follow-ups, and analyze conversion data, freeing up human resources to focus on strategy rather than administrative tasks. Similarly, individuals can integrate these tools with email, calendars, or project management apps to streamline daily routines, saving hours of repetitive work each week.
The evolution of automation software reflects broader trends in technology. Early automation tools were limited to single-function tasks like data entry or report generation. In contrast, today’s AI-powered automation platforms can orchestrate multi-step processes, integrate with multiple systems, and even predict potential workflow bottlenecks before they occur. Companies like UiPath, Automation Anywhere, and Zapier have pushed the boundaries, demonstrating how intelligent automation can increase productivity by up to 40–50% in certain business operations.
Additionally, smart automation software is not confined to large enterprises. Small businesses and startups are increasingly adopting these tools to remain competitive, manage growth efficiently, and reduce manual errors. The software’s ability to learn from patterns, suggest optimizations, and adapt to changing conditions makes it invaluable in today’s fast-paced digital environment.http://aibygoogl.com
Overall, smart automation software represents a significant leap forward in how humans and machines collaborate. By automating repetitive and rule-based tasks while providing insights for strategic decisions, it allows both businesses and individuals to work smarter, not harder.
How Smart Automation Software Works
Smart automation software is not just a tool that completes repetitive tasks—it’s an intelligent system that understands workflows, learns from data, and optimizes processes dynamically. The effectiveness of smart automation comes from a combination of advanced technologies, algorithms, and integration capabilities that allow it to act autonomously while adapting to changing conditions.
Core Technologies Behind Smart Automation Software
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
AI is the brain of smart automation software. It allows the system to analyze patterns, predict outcomes, and make informed decisions. Machine learning enables the software to improve its performance over time by learning from previous interactions. For instance, in customer support automation, the software can identify frequently asked questions and automatically provide answers, gradually refining its responses based on user feedback. - Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
RPA allows smart automation software to replicate human actions within digital systems. Tasks such as filling out forms, transferring data between systems, or processing invoices can be handled efficiently by bots. Unlike basic RPA, when combined with AI, the bots can make contextual decisions rather than simply executing predefined steps. - Workflow Orchestration and Integration Tools:
Smart automation software coordinates multiple systems, apps, and data sources. Workflow orchestration ensures that tasks flow seamlessly across departments or platforms, reducing delays and eliminating bottlenecks. For example, an order processing workflow can automatically notify inventory, finance, and shipping teams once a customer places an order. - Data Analytics and Predictive Automation:
These tools analyze historical and real-time data to predict trends, identify anomalies, and recommend actions. Predictive automation allows the system to preemptively handle potential issues, such as alerting a sales team about delayed leads or suggesting optimal scheduling for projects based on past performance.
How Smart Automation Software Understands Tasks
Smart automation software breaks down tasks into a series of steps, identifies patterns, and applies algorithms to execute them efficiently:
- Task Recognition: The software analyzes inputs from users, databases, or systems to identify what needs to be done.
- Decision-Making Algorithms: Based on rules and AI insights, it decides the best way to complete the task.
- Adaptive Learning: By observing outcomes and receiving feedback, the software improves its future performance.
- Exception Handling: Smart automation systems can detect errors or unexpected conditions and either correct them automatically or escalate them to a human operator.
Example: In an invoicing workflow, smart automation software can automatically generate invoices, send reminders to clients, reconcile payments, and flag discrepancies without human intervention. Over time, it can learn to optimize invoice scheduling, detect recurring errors, and suggest improvements for faster payments.
By combining these technologies, smart automation software transforms routine workflows into dynamic, self-optimizing processes. It doesn’t just reduce manual effort; it provides actionable insights, improves accuracy, and ensures consistent operational efficiency.
Popular Smart Automation Software in 2026
In 2026, smart automation software has reached new levels of sophistication, catering to a wide range of business sizes, industries, and workflows. Whether for enterprises, startups, or niche industries, automation tools are transforming productivity, efficiency, and decision-making. Let’s explore some of the most popular solutions and their applications.
Enterprise-Focused Tools
Large organizations require automation solutions that can handle complex processes, integrate with multiple systems, and scale across departments. Popular enterprise automation tools include:
- UiPath: A leading RPA platform that enables organizations to automate repetitive tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer support workflows. UiPath combines AI and ML to improve automation accuracy over time.
- Automation Anywhere: Offers intelligent automation for business processes, including finance, HR, and IT operations. Its Bot Store allows businesses to deploy pre-built bots quickly.
- Blue Prism: Focused on enterprise-grade RPA, Blue Prism provides scalable automation solutions with strong governance and security features, making it ideal for highly regulated industries like banking and healthcare.
Benefits for Enterprises:
- Reduces operational costs
- Improves accuracy and compliance
- Enhances employee productivity by removing mundane tasks
- Provides analytics for process optimization
SMB and Startup Automation Tools
Small businesses and startups often need affordable, easy-to-use automation solutions that integrate with their existing tools. Popular options include:
- Zapier: Connects over 5,000 apps, allowing businesses to automate workflows without coding. For example, automatically adding new leads from forms to a CRM or sending notifications to a team chat app.
- Make (formerly Integromat): Enables complex automation scenarios with visual workflow builders. It’s ideal for startups that require flexibility in automating marketing, sales, and operations.
- Workato: Provides low-code integration and automation for SMBs, combining workflow orchestration with AI-driven insights.
Benefits for SMBs:
- Saves time on repetitive tasks
- Reduces manual errors
- Enables teams to focus on growth and innovation
Industry-Specific Automation Software
Certain industries require specialized automation solutions to meet regulatory requirements, handle complex data, or streamline unique workflows:
- Healthcare: Automation tools like Olive AI manage administrative tasks, appointment scheduling, and patient data entry, reducing errors and increasing efficiency.
- Finance: Tools like Kofax automate invoicing, reconciliation, and compliance reporting, ensuring accuracy and faster processing.
- Manufacturing: Platforms like Siemens Mendix provide automation for production workflows, inventory management, and supply chain optimization.
- Retail: Smart automation software helps with order processing, inventory tracking, and personalized marketing campaigns.
Table: Comparison of Popular Smart Automation Software
| Tool | Target Audience | Key Feature | Industry Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| UiPath | Enterprise | RPA + AI workflow | Multi-industry |
| Automation Anywhere | Enterprise | Pre-built bots + analytics | Finance, HR, IT |
| Blue Prism | Enterprise | Scalable RPA | Regulated industries |
| Zapier | SMB/Startup | App integrations | General business |
| Make | SMB/Startup | Visual workflow automation | General business |
| Workato | SMB/Startup | Low-code automation | Marketing, Sales |
| Olive AI | Healthcare | Admin and patient workflow automation | Healthcare |
| Kofax | Finance | Invoicing & compliance automation | Finance |
| Siemens Mendix | Manufacturing | Production & supply chain automation | Manufacturing |
By understanding the variety of smart automation software available in 2026, businesses of all sizes can select the right tools for their needs. From large-scale enterprise systems to nimble SMB solutions and industry-specific platforms, these tools offer unmatched efficiency, accuracy, and insights.
Key Benefits of Smart Automation Software
Smart automation software is designed to not only reduce manual effort but also to improve accuracy, efficiency, and overall business performance. Its adoption has transformed both individual productivity and organizational workflows. Understanding these benefits is crucial for businesses and teams looking to maximize ROI from automation tools.
Benefits for Businesses
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency
By automating repetitive tasks such as data entry, report generation, and customer follow-ups, businesses can free employees to focus on higher-value activities. According to a 2025 report by Deloitte, companies using automation tools reported a 30–50% increase in workflow efficiency within the first year of adoption. - Cost Reduction and Improved ROI
Automation reduces the need for manual labor on repetitive processes, lowering operational costs. For example, UiPath reported that businesses implementing RPA across finance and HR departments saved an average of $150,000 annually per process automated. - Error Reduction and Quality Improvement
Human errors in repetitive tasks like invoice processing or data transfer can be costly. Smart automation software ensures consistent, accurate execution, reducing compliance risks and improving overall quality. - Data-Driven Insights and Analytics
Many smart automation platforms include analytics dashboards that track workflow performance, identify bottlenecks, and provide actionable insights. Businesses can leverage these insights to optimize processes and make informed strategic decisions.
Benefits for Individuals and Teams
- Time-Saving and Workload Reduction
Automation software helps teams and individuals handle routine tasks faster, such as scheduling meetings, sending notifications, or syncing data across apps. For instance, Zapier users often report saving 5–10 hours per week by automating workflows that previously required manual input. - Task Prioritization and Organization
Smart automation platforms can categorize tasks, set reminders, and even trigger actions based on priority or deadlines. This ensures that critical activities are addressed promptly while routine tasks are handled automatically. - Seamless Integration with Everyday Tools
Modern automation tools integrate with email, calendars, CRMs, and project management apps. This interconnected ecosystem allows teams to automate multi-step workflows without switching between multiple platforms, improving collaboration and reducing friction.
Quantifiable Impacts of Smart Automation
| Metric | Without Automation | With Smart Automation | Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average time spent on repetitive tasks/week | 15 hrs | 5 hrs | 66% reduction |
| Error rate in manual processes | 7% | 1% | 85% reduction |
| Employee productivity | Baseline | +40% | Significant increase |
| Operational cost for routine workflows | $100,000/year | $60,000/year | 40% cost savings |
Case Study 1 – UiPath in Financial Services:
A mid-sized bank implemented UiPath to automate loan processing. Within six months, processing time per application dropped from 3 days to 6 hours, while errors were reduced by 70%, resulting in faster approvals and improved customer satisfaction.
Case Study 2 – Zapier in Startups:
A SaaS startup used Zapier to automate lead tracking and customer onboarding. By connecting their CRM, email marketing, and support platforms, the team saved over 8 hours per week, allowing staff to focus on product development and customer engagement.
Challenges and Limitations of Smart Automation Software
While smart automation software offers significant benefits, it is not without challenges. Businesses and individuals must understand potential limitations to ensure successful adoption and avoid common pitfalls.
1. Implementation Costs and Resource Requirements
Deploying smart automation software often requires a substantial investment, including licensing fees, infrastructure setup, and training. While the ROI can be high, small businesses may find initial costs challenging. Enterprise systems like UiPath or Automation Anywhere often require dedicated IT teams for deployment and maintenance.
2. Integration and Compatibility Challenges
Automation software must work seamlessly with existing tools, databases, and enterprise systems. Incompatibility can lead to workflow disruption, requiring additional customization or middleware. For example, connecting legacy ERP systems with modern automation platforms can involve complex integration efforts.
3. Employee Adaptation and Training
The adoption of automation can be met with resistance from employees due to fear of job displacement or unfamiliarity with new systems. Training programs are essential to help teams understand how to leverage smart automation software effectively. Studies show that 40% of failed automation projects result from inadequate training and employee engagement.
4. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Smart automation software often handles sensitive data, from customer information to financial records. Without proper security protocols, there is a risk of data breaches, compliance violations, and cyberattacks. Businesses must ensure that automation platforms adhere to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 to protect data integrity.
5. Limitations of AI-Based Automation
While AI enhances automation, it is not infallible. AI-driven systems may misinterpret complex instructions, fail to adapt to rare exceptions, or produce biased outputs if trained on flawed data. Human oversight remains crucial, especially in high-stakes processes like healthcare, finance, and legal operations.
6. Dependence on Internet and Cloud Services
Many automation platforms rely on cloud-based services for processing and data storage. Unstable internet connections or cloud outages can interrupt workflows, which may affect productivity and business continuity. Offline capabilities or hybrid solutions can mitigate this risk but may add complexity and cost.
Example:
A global financial services company implemented a smart automation system for invoice processing. While it reduced manual effort by 60%, integration issues with legacy ERP systems initially caused delays, highlighting the importance of planning and testing before full deployment.